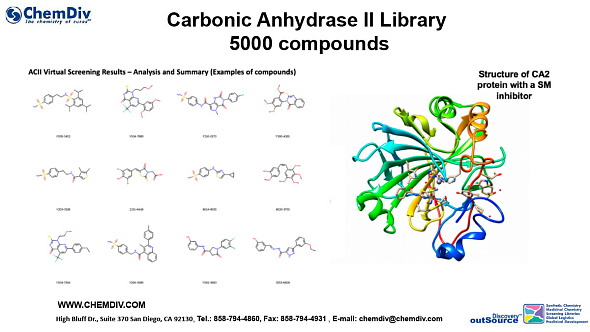
Carbonic Anhydrase II Library
Carbonic Anhydrase II Inhibitors Library
ChemDiv designed a novel library comprising 5,000 compounds selectively inhibiting the carbonic anhydrase II enzyme.
Carbonic Anhydrase II (CA II) is a crucial enzyme in the human body, primarily responsible for regulating acid-base balance and carbon dioxide transport. It catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide into bicarbonate and protons, a reaction fundamental to many physiological processes, including respiration, ion transport, and pH homeostasis. CA II is found in various tissues throughout the body, with particularly high concentrations in red blood cells, where it facilitates the efficient exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen during blood circulation. Its dysfunction is associated with several diseases, such as renal tubular acidosis and osteopetrosis, due to its role in kidney and bone metabolism. CA II is a potential target for therapeutic drugs, especially diuretics and anti-glaucoma agents. Research into CA II continues to provide insights into its biochemical mechanisms and potential for treating various health conditions.
Currently, there are several approved drugs on the market used for the treatment of high intraocular pressure, seizures, migraines, and as diuretics.
CA II is being extensively investigated as a target for novel therapeutics, as indicated by a rapidly growing number of research publications on PubMed, distinct publications that have deposited structures in the PDB database, and more than 12K associated ligands in the Chembl database.
The main steps of the ACII Virtual Screening include:
1. Substructure Search: This step presumes identifying compounds with specific chemical structures or features (chemotypes) known to interact with CA II.
2. Docking of Compounds: Docking approximately 10,000 compounds from ChemDiv's stock to the binding site of CA II is a realistic scale for virtual screening. This process involves computationally predicting how small molecules, such as drugs, bind to an enzyme.
3. Selection Based on Docking Scores: Selecting around 6,000 compounds based on ICM docking scores (< -20.0) and Flare scores (< -7) is a standard method. These scores help in predicting the binding affinity of compounds. H
4. Electrostatic Complementarity Calculation: This step involves assessing how well the electronic properties of the small molecules complement the target enzyme. A cutoff for correlation > 0.1 is mentioned, but the relevance of this specific value should be contextually verified.
5. Physicochemical Properties Prediction: Using ICM models to predict the physicochemical properties of compounds is a crucial step in ensuring the drug-likeness and viability of the molecules.
6. Final Selection: The process concludes with a final selection of approximately 5,000 compounds specifically targeting CA II. This number seems consistent with the initial filtering steps.
ChemDiv designed a novel library comprising 5,000 compounds selectively inhibiting the carbonic anhydrase II enzyme.
Carbonic Anhydrase II (CA II) is a crucial enzyme in the human body, primarily responsible for regulating acid-base balance and carbon dioxide transport. It catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide into bicarbonate and protons, a reaction fundamental to many physiological processes, including respiration, ion transport, and pH homeostasis. CA II is found in various tissues throughout the body, with particularly high concentrations in red blood cells, where it facilitates the efficient exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen during blood circulation. Its dysfunction is associated with several diseases, such as renal tubular acidosis and osteopetrosis, due to its role in kidney and bone metabolism. CA II is a potential target for therapeutic drugs, especially diuretics and anti-glaucoma agents. Research into CA II continues to provide insights into its biochemical mechanisms and potential for treating various health conditions.
Currently, there are several approved drugs on the market used for the treatment of high intraocular pressure, seizures, migraines, and as diuretics.
CA II is being extensively investigated as a target for novel therapeutics, as indicated by a rapidly growing number of research publications on PubMed, distinct publications that have deposited structures in the PDB database, and more than 12K associated ligands in the Chembl database.
The main steps of the ACII Virtual Screening include:
1. Substructure Search: This step presumes identifying compounds with specific chemical structures or features (chemotypes) known to interact with CA II.
2. Docking of Compounds: Docking approximately 10,000 compounds from ChemDiv's stock to the binding site of CA II is a realistic scale for virtual screening. This process involves computationally predicting how small molecules, such as drugs, bind to an enzyme.
3. Selection Based on Docking Scores: Selecting around 6,000 compounds based on ICM docking scores (< -20.0) and Flare scores (< -7) is a standard method. These scores help in predicting the binding affinity of compounds. H
4. Electrostatic Complementarity Calculation: This step involves assessing how well the electronic properties of the small molecules complement the target enzyme. A cutoff for correlation > 0.1 is mentioned, but the relevance of this specific value should be contextually verified.
5. Physicochemical Properties Prediction: Using ICM models to predict the physicochemical properties of compounds is a crucial step in ensuring the drug-likeness and viability of the molecules.
6. Final Selection: The process concludes with a final selection of approximately 5,000 compounds specifically targeting CA II. This number seems consistent with the initial filtering steps.