MEF2-HDAC (class II) Modulators Library
ChemDiv’s MEF2-HDAC Modulators Library contains 4,805 compounds.
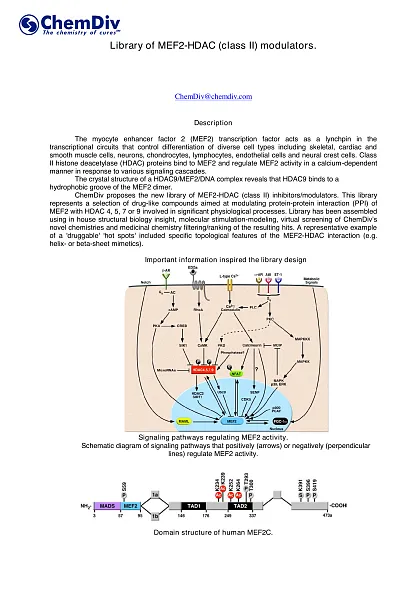
The Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2 (MEF2) transcription factor serves as a lynchpin component in the transcriptional circuits that control the differentiation of various cell types, including skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle cells, as well as neurons, chondrocytes, lymphocytes, endothelial cells, and neural crest cells. Class II Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) interact with MEF2, regulating its activity in a calcium-dependent manner in response to diverse signaling cascades. The crystal structure of an HDAC9/MEF2/DNA complex has revealed that HDAC9 attaches to a hydrophobic groove on the MEF2 dimer.
By modulating the interaction between MEF2 and HDACs, targeted compounds can affect critical physiological processes such as muscle differentiation, neuronal activity, and cardiovascular development. Targeting the MEF2-HDAC pathway offers a therapeutic avenue for diseases where those pathways are dysregulated, including certain muscular disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and heart conditions. The development of specific MEF2-HDAC modulators can lead to drugs that precisely target these pathways, minimizing side effects associated with broader acting drugs. Consequently, research in MEF2-HDAC modulators is an area of high interest in the pharmaceutical industry, offering novel treatment options for a variety of health conditions.
ChemDiv has developed a new library of small molecule inhibitors and modulators targeting the MEF2-HDAC (class II) interaction. This collection comprises drug-like compounds designed to modulate the protein-protein interaction between MEF2 and HDACs 4, 5, 7, or 9, which play crucial roles in vital physiological processes. This library has been curated using ChemDiv's in-house structural biology insights, molecular modeling and stimulation, and virtual screening of novel chemical entities. This workflow includes medicinal chemistry techniques of filtering and ranking of the potential hit molecules. A key beneficial characteristic of our library is its focus on the 'druggable' 'hot spots' within the MEF2-HDAC interaction, featuring specific topological attributes such as helix- or beta-sheet mimicry.