BioNxt Reports Final Preclinical Results Demonstrating Approximately 40% Higher Cladribine Delivery for the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
BioNxt Solutions Inc. is pleased to report final results from a preclinical pig study demonstrating that its proprietary needle-free, swallow-free sublingual oral dissolvable film (ODF) cladribine formulation for the treatment of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) achieved significantly higher systemic drug delivery than a conventional oral tablet formulation of cladribine.
Such tablets are used in commercially successful therapies like Mavenclad®, which has reported annual global sales exceeding USD 1.2 billion and sustained double-digit growth.
Development Milestone and Clinical Rationale
The results represent an important development milestone for BioNxt. Demonstrating in a robust large-mass non-rodent model that reformulating cladribine as a sublingual oral dissolvable film can materially improve systemic drug delivery compared with conventional oral tablet dosing is significant.
By directly comparing two fundamentally different routes of administration under controlled conditions, the study helps de-risk the clinical development and commercialization pathway. This supports the rationale for advancing the sublingual ODF formulation into human pharmacokinetic studies.
Final Study Results: Validation of Delivery Efficiency
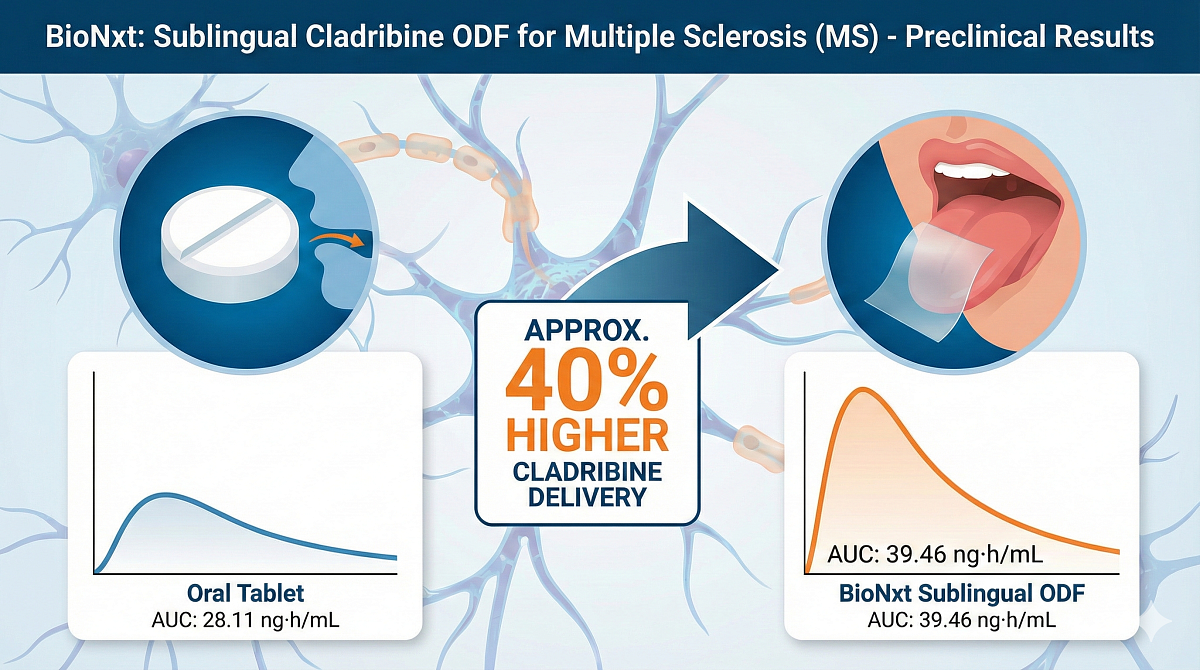
The completed preclinical pig study showed that BioNxt's cladribine sublingual oral dissolvable film achieved meaningfully higher systemic drug availability than the conventional oral tablet formulation. Under the study conditions, BioNxt's proprietary sublingual ODF delivered approximately 40% higher cladribine exposure, highlighting a clear and clinically relevant improvement in delivery efficiency.
Systemic exposure was assessed over a 48-hour period using AUC (0-48 h), a widely accepted calculated measure based on repeated blood concentration measurements that reflects how much drug reaches the bloodstream and how long it remains there.
Quantitatively, the mean AUC (0-48 h) for the sublingual ODF was 39.46 ng·h/mL, compared with 28.11 ng·h/mL for the oral tablet formulation. This difference demonstrates a substantial increase in total drug exposure over time following sublingual administration.
Interpreting Systemic Drug Exposure (AUC)
AUC is a calculated value based on repeated blood measurements taken over time after drug administration. Unlike a single peak measurement, AUC captures both the extent of absorption and the duration of exposure, making it the most informative pharmacokinetic parameter for comparing how effectively different formulations or routes of administration deliver a drug.
Future Implications: Dose Optimization
In this study, the approximately 40% higher AUC observed for BioNxt's sublingual ODF indicates that a greater amount of cladribine reached systemic circulation and was maintained for a longer period. This finding supports the conclusion that the sublingual delivery approach provides more efficient and consistent overall drug availability.
Importantly, improved delivery efficiency may also support dose optimization in future studies, with the potential to reduce systemic drug burden at equivalent therapeutic exposure. This could, in turn, improve tolerability and reduce side effects—an outcome BioNxt intends to evaluate in planned clinical development.